


Decentralized Docker-Based Virtual Machine
Orbs VM is a dedicated and decentralized virtual machine, similar in concept to AWS EC2 - only decentralized.
Orbs VM services are implemented as Docker containers, deployed to the Orbs Network and then executed by the network validators. Much like AWS EC2 container services, there is minimal devops involved as orchestration is automated. Unlike AWS EC2, the protocol is fully transparent and decentralized, providing execution guaranteed to the user community by relying on dozens of independent network validators that participate in the protocol.
Any Programming Language
Services in Orbs VM are implemented as an industry standard container - Docker. As such, they can rely on any familiar programming language like Go, C++, Rust, JavaScript, Python and Java. Developers are not required to learn unfamiliar smart contract languages or operate strange toolchains - they can rely on their existing knowledge.
Always On
Just like regular Docker containers, Orbs VM services are always-on. They are not event-driven and do not become dormant when unused. Any event-driven logic can be implemented inside the container by implementing the logic that scans continuously for the desired condition. For example, services can monitor any number of L1 blockchains by continuously reading new published blocks and analyzing their content.
Enhance Existing Smart Contracts
Orbs VM is not meant to replace existing L1 smart contracts. It is a complementary solution that allows developers to enrich their business logic with actions that the smart contract sandbox is unable to do, without sacrificing decentralization. Dapps that currently rely on their own centralized backends are welcome to migrate these backends to Orbs VM and eliminate the centralized bottlenecks from their offering.
Alternatives
Before trying Orbs VM, please consider Orbs Lambda - a solution designed for ease of use that resembles AWS Lambda. Orbs VM is more difficult to use, but is more flexible and designed for complex use-cases that require the service to be always-on or require non-JavaScript dependencies.
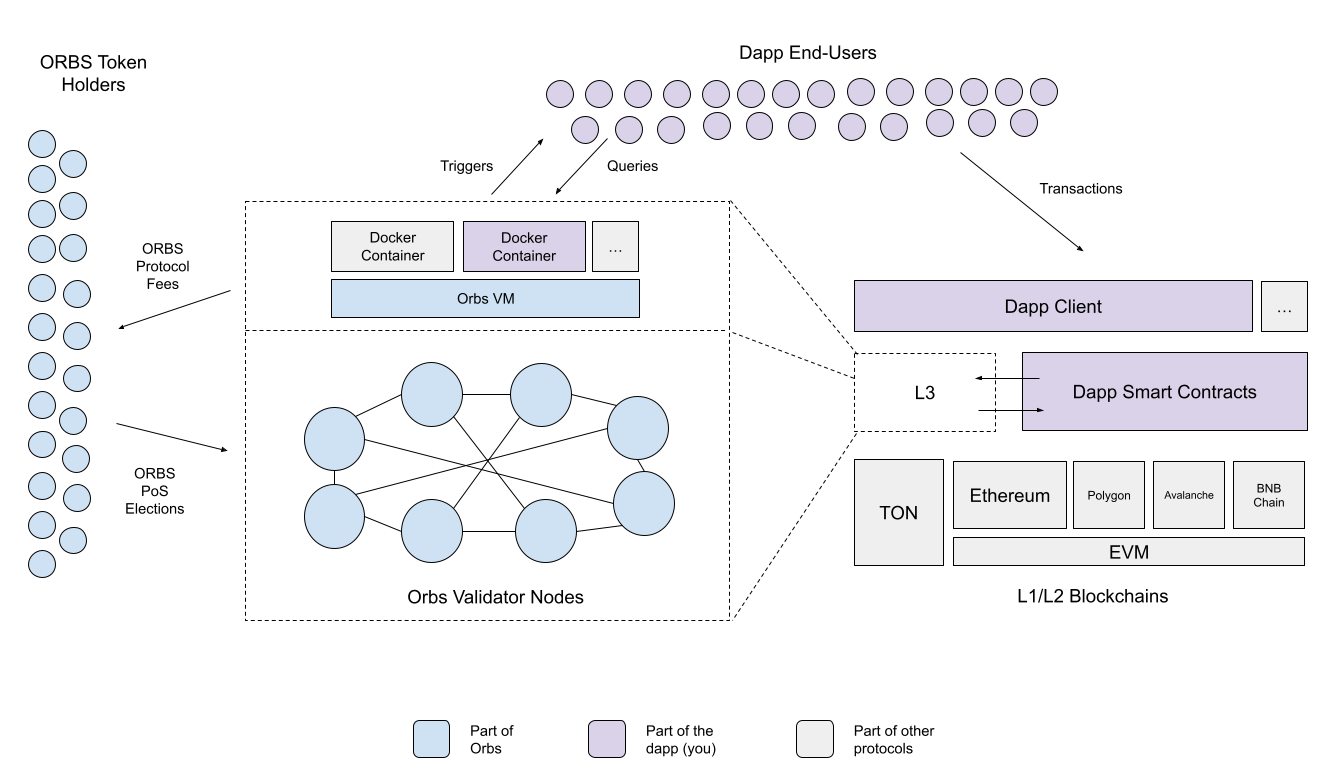
The Orbs Network includes dozens of independent validators that run Proof-of-Stake consensus and execute Orbs VM Docker containers in a decentralized manner.
Orbs is not an L1 blockchain and is not trying to replace existing smart contracts. It is more accurately described as an oracle network similar to Chainlink, operating in L3. Orbs runs over leading L1/L2 blockchains like the EVM and TON and allows dapps to enhance smart contracts with advanced capabilities that are unsupported by the sandboxed L1/L2 smart contract model.
Orbs VM is designed to enhance the capabilities of existing smart contracts. Here are some real world examples of how dapps are using this infrastructure. Notice that many of these examples could have been implemented with a centralized backend operated by the dapp itself, but this would create a centralized bottleneck that can be avoided by using the dozens of validators of Orbs Network.
Most of these examples can also be implemented using Orbs Lambda assuming the implementation meets its limitations (like relying on JavaScript only). Orbs Lambda is simpler to work with but less flexible. Any use-case that can be implemented by Orbs Lambda can also be implemented by Orbs VM. Orbs Lambda itself is actually implemented using Orbs VM.
Price feed similar to Chainlink or any other data oracle
An Orbs VM container is free to fetch any data available online and is not limited to current on-chain state. External market price feed is a useful example of such data that can be read from a multitude of exchanges and price providers (Coinbase, Binance, CoinMarketCap, Coingecko, etc). The container continuously queries the price from all external sources, then signs the price off-chain and sends the signatures to a new dapp smart contract that verifies the Orbs quorum and records an aggregated price on-chain.
Mobile push notifications for dapp end-users for on-chain events
A dapp like Aave or Compound may want to alert its users when an on-chain condition is triggered - for example before their positions are in danger of being liquidated. An Orbs VM container monitors every block and checks if any of the positions passes a liquidation threshold and if so, triggers a mobile push notifications webhook, a tweet or a Telegram/Discord chat message. A more advanced version of this container will also generate an on-chain transaction to reduce the position in the protocol automatically to avoid liquidation completely by adjusting it according to the live market price.
Calculating a staked vote according to historic balance snapshot on multiple chains
An Orbs VM container can access on-chain data. Unlike smart contracts, it is not limited to the state head and can also query historic balances. Unlike smart contracts, it is also not limited to the same blockchain and can query multiple blockchains like Ethereum, Polygon and BNB Chain. Governance votes in dapps usually rely on a historic balance snapshot to avoid vote manipulation by buying tokens after the vote was announced. Dapp users often exist on multiple blockchains since tokens are often bridged. If the vote passes, the container can generate an on-chain transaction - a great way to implement decentralized smart contract upgrades.
Auto compounding of vaults like Harvest.finance or other advanced strategies
Vaults are decentralized "hedge funds" that implement a DeFi investment strategy on-chain in a completely trustless manner using smart contracts. Efficient investment strategies often require automatic triggers that adjust the position in some way. One example is auto compounding - selling rewards back to the base assets and re-depositing them to increase the position principal. Another example is comparing two alternative positions and moving funds automatically according to the one with the best APR. The container checks for relevant triggers by monitoring every new block and generates the transaction to trigger the appropriate response on-chain when the position needs to be adjusted.
Executing large trades in DeFi without price impact by implementing TWAP
Trades executed on on-chain DEX/AMM protocols are atomic and take place immediately. When the trade is relatively large or relies on a low liquidity pair, this can result in significant loss due to price impact. An Orbs VM container can break the single trade into multiple smaller ones every several minutes, allowing enough time for arbitrageurs to correct the pair back to market price, thus reducing price impact. The container will generate the numerous transactions to carry the smaller trades and adjust price limits according to live market prices to avoid front running.
The development process of a new Orbs VM service includes the following steps:
Want to learn more about the Orbs network? Check out the developers documentation here, or chat with the Orbs team on the official Telegram channel and on Discord.
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. By continuing to use our site, you accept our cookie policy.