


The past several years have brought new levels of sophistication to the DeFi space, with over $1B in daily trading volume executed across DEXs and AMMs. At the same time, due to the inherently limited capabilities of smart contracts, DeFi markets lack features that could help manage the heightened volatility and liquidity issues that characterize the current crypto landscape.
Orbs pioneers the concept of L3 infrastructure, by utilizing Orbs’ decentralized network to enhance the capabilities of existing EVM smart contracts. Using Orbs validators as decentralized bidders, the project is introducing a new decentralized dTWAP (Decentralized Time-Weighted Average Price) protocol for DEX/AMMs, which allows for advanced time-spread trades to be executed on these platforms in a decentralized manner.
This blog outlines the concept and architecture behind Orbs’ new decentralized dTWAP protocol that will allow DEXs to harness this technology to benefit the platform and its users.
TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price) is a common algorithmic trading executing strategy in CeFi that seeks to minimize a large order’s impact on the market by dividing it into a number of smaller trades and executing these trades at regular intervals over a specified period of time.
There are two primary benefits of utilizing TWAP trading strategies.
1. Price Impact Reduction
TWAP strategies reduce the impact of an order on the general market price.
One scenario where price impact causes significant losses to traders is with large orders. Nonetheless, even smaller orders can suffer from price impact, particularly when the trading pair is long-tail and low liquidity.
The problem of an individual trade having a disproportionate effect on the market, for either of these reasons, can be especially acute in DeFi where liquidity is much more fragmented than it is in the traditional financial markets. This fragmentation often exists even within individual dominant DEXs such as QuickSwap, which offer multiple pools for the same trading pairs.
Even TWAP strategies with relatively short durations (i.e., executing a trade in intervals of 1-2 minutes over a period of 15-20 minutes) can mitigate this problem by giving arbitrageurs a short window to close any price discrepancies on the affected pools and bring the reserves back to equilibrium (on par with spot price).
In addition to benefiting traders, this type of TWAP strategy also benefits the trading platform itself, as minimizing the risk of price impact can lead to increased liquidity on the pool and thus increased trading volume.
2. Automation of Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA)
Dollar-cost averaging (DCA) is an investing strategy where the investor purchases an asset or set of assets having a certain dollar value on a specific schedule (i.e., on the first day of every month). The goal behind DCA is to average out abnormal market conditions and lessen the impact of volatility on the overall purchase.
TWAP trades can be used to generate an automated version of this strategy, typically by entering a market order with longer intervals that lasts for a longer period of time or even perpetually. This trade can essentially serve as an automated DCA bot that requires no additional action from the investor.
While the benefits of dTWAP transactions are clear, the current limitations of EVM smart contracts make them impossible to implement in a decentralized manner. Orbs’ L3 infrastructure solves this problem using the new dTWAP protocol in a fully decentralized and secure way.
The dTWAP smart contract architecture defines 2 actors:
Maker: User, the Order creator.
Taker: Incentivized independent participators that monitor Orders submitted by makers
One honest taker (i.e., a taker who is willing to set the fee at the minimum amount needed to cover gas costs) is enough to ensure the entire system functions effectively at spot prices.
The dTWAP Smart Contract does not hold any funds, has no owners, administrators or other roles and is entirely immutable once deployed on an EVM blockchain.
The entire process is described in the following flow chart:
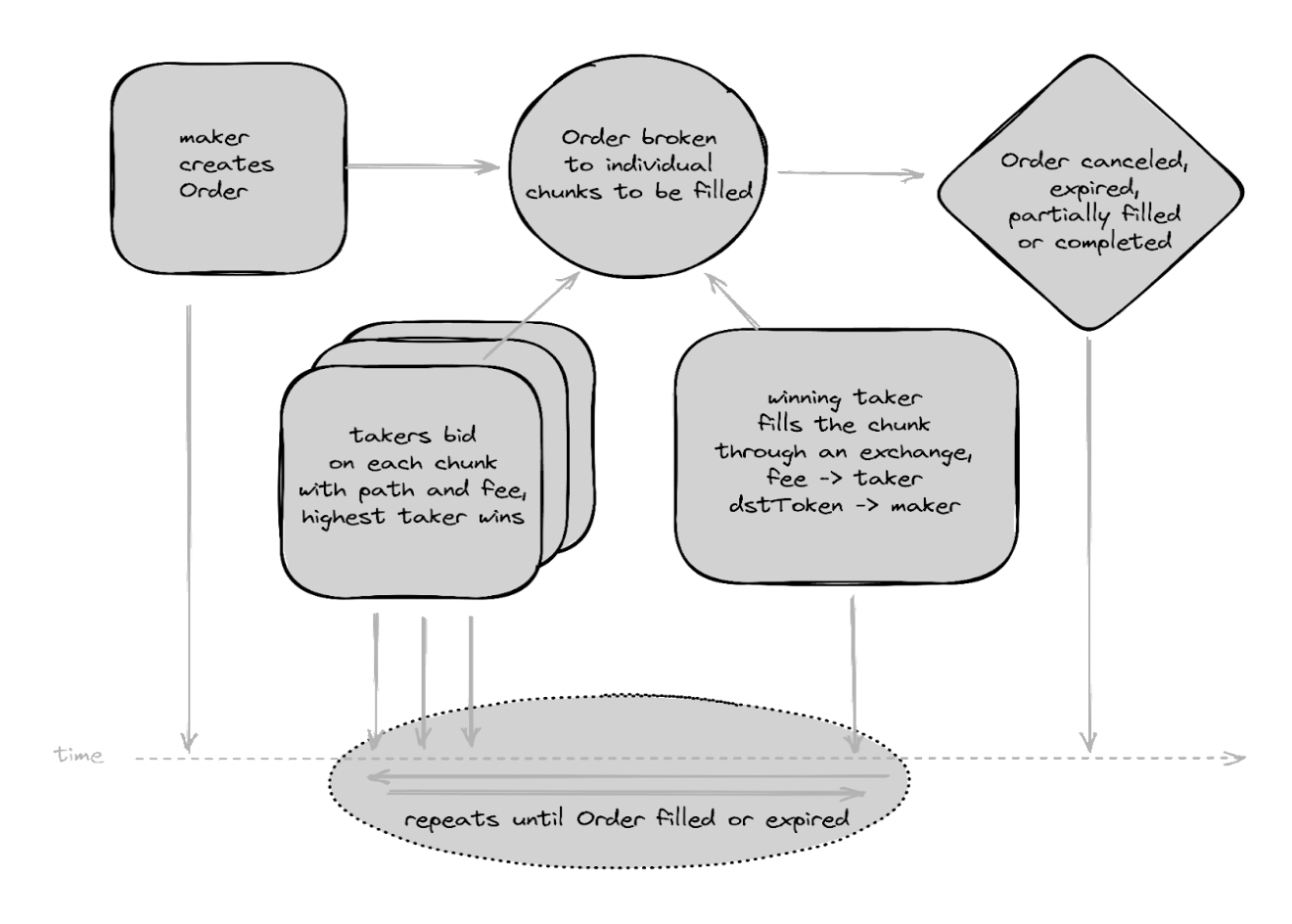
The Orbs Network is an open, decentralized and public blockchain infrastructure executed by a secure network of permissionless validators (known as “Guardians”) using Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus. Orbs is optimized to provide “L3” services, working in conjunction with existing L1 and L2 layers and acting as a “decentralized backend” that enhances the capabilities of EVM smart contracts. Orbs Network mainnet is live since 2019 and has dozens of active validators staked with over $100M.
The network provides its L3 services by operating as a decentralized serverless cloud that allows developers to design applications that extend the capabilities of their smart contracts without relying on traditional centralized server solutions. These applications are deployed to be executed by the Orbs Guardians in a decentralized way.
As part of the dTWAP protocol, Orbs Guardians will run a tailored function utilizing ORBS-Lambda that acts as the single honest bidder, or “taker”, that is required for the dTWAP protocol to run optimally and achieve prices that track the spot market price as closely as possible.
The application run by Orbs Guardians will, in a decentralized manner, monitor the dTWAP Smart Contract. When an order has been sent and a chunk is open for bids, Orbs Guardians will automatically calculate and submit an honest bid. The fee component of the bid will include only a request to be estimated for the estimated gas fees. In addition, the Guardians will determine the optimal path for the transactions using services such as ParaSwap API, or the DEXs own router.
By automatically creating honest bids that are hardcoded to only specify a minimal gas fee and optimal trade path, Orbs Guardians will provide a strong level of assurance that the trades executed and the dTWAP contract track spot market prices as closely as possible.
In addition, the Orbs team has designed a specialized UI that can be easily integrated and customized by any DEX, to create an intuitive, user-friendly and informative way for users to set the parameters for and initiate dTWAP trades.
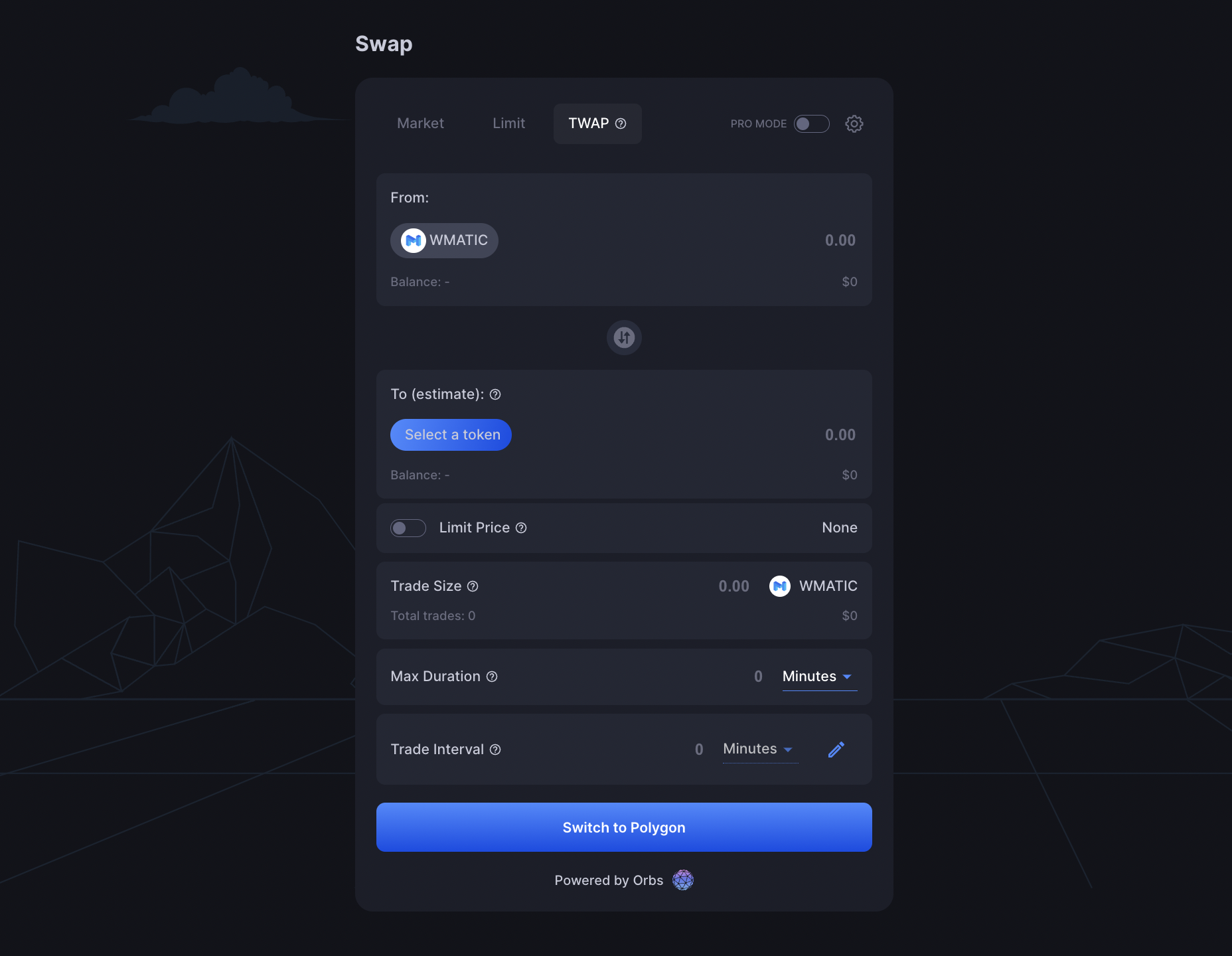
dTWAP trades can be divided into market orders and limit orders. In a market dTWAP order, the trader sets parameters, the size of the desired trade, the total duration of the strategy, and the intervals between individual trades. The trades are then executed at the predetermined intervals at the best available current market price.
Limit orders are similar, except that in these strategies, the trader sets a limit on the price at which trades will be executed. If a price within the limit is not available at a given interval, the individual trade will not be executed. In this version of the strategy, the larger total order may only be executed partially by the end of the duration period.
The dTWAP UI has 3 basic parameters which the user needs to specify:
These parameters allow for a lot of flexibility for the user when placing the order, to take into account factors such as market conditions, current gas fees, etc. Once all of these parameters are set, the user will have the ability to Approve the specific source token and place the order.
Harnessing the ability of Orbs’ unique L3 infrastructure to expand the capabilities of DeFi platforms can allow DEXs to provide highly efficient dTWAP orders to its user base without sacrificing decentralization. With Orbs’ decentralized backend ensuring that dTWAP orders are executed at an optimal price and at fair fees, this type of trade can become a viable option for DEX users, giving them a number of new ways to make their trading activities more sophisticated. In turn, DEXs themselves can benefit from increased liquidity and attract new users by offering features that are currently unavailable on competing DEXes that do not utilize this technology.
More Info and Relevant Links
dTWAP protocol Github: https://github.com/orbs-network/twap
Security audits: PeckShield, RD Auditors
General information about Orbs L3: https://www.orbs.com/network/
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. By continuing to use our site, you accept our cookie policy.